Dokuwiki in Kubernetes
Installing Dokuwiki on Kubernetes
Previously, I had a post here with steps to install Dokuwiki with Docker. If you have a suitable Kubernetes platform, proceed. If you are not familiar with Kubernetes, see a post on the topic. I also have not been doing many homelab projects. Using Kubernetes to run and test apps has been a very stable experience and I haven’t needed to do much of anything to keep it running. Now I am going to move my Dokuwiki into Kubernetes.
Requirements
In order to proceed, you must have a k8s platform, the kubectl command line utility, and a persistent storage volume.
I recommend creating a Kubernetes namespace for the wiki resources:
|
|
Dokuwiki manifests
In order to deploy Dokuwiki onto a Kubernetes cluster, the deployment needs to be configured in YAML format document. This defines all of the resources that will be created in the Kubernetes cluster in order to run your application. In this case for Dokuwiki, we need to create a container that runs the Dokuwiki server, a storage volume to store the files that are created for each wiki page, a service exposes the network port used for the Dokuwiki server, and an ingress which is used to route network traffic from outside the cluster to the Dokuwiki service and container.
dokuwiki-pvc.yaml
This file will request persistent storage for the wiki container(s). This will utilize the longhorn storage provider. For more information, see a previous post on the topic. You can use any Kubernetes storage class just make sure to specify the correct value in the config below.
|
|
dokuwiki-deployment.yaml
|
|
Apply these manifests
Use these files to deploy a PersistentVolumeClaim and the Deployment to your cluster:
|
|
The -n wiki is to deploy the resources in the namespace created earlier.
Verify the objects are ready:
|
|
|
|
Create an in cluster service object
Once the deployment is ready (which means the PVC was bound also), a Service object is needed to route traffic to the Dokuwiki container.
Enter the following command with the kubectl utility to create a cluster service object that can be used to route traffic to the pods.
|
|
View the newly created object:
|
|
The output should be similar:
|
|
Note that these are IP addresses on the Kubernetes cluster private network and are not externally accessible without creating a load balancer or similiar resource.
Next are a few optional steps that include setting up a certificate and Ingress to access the wiki from outside the cluster. If you want to skip those steps, you can change the previous command to create a service type NodePort which will allow you to access the wiki by using the IP or hostname of a Kubernetes node followed by the port assigned in the NodePort service in your browser:
|
|
Example browser URL: http://k8s-node-ip-or-hostname:nodeport_port_number_here
Creating a TLS certificate
I use a wildcard certificate for my local area network. For information on how to obtain something similar, check out a post on the topic. This resource is optional, if you do not want to use HTTPS and encrypt the connection from clients to the wiki, omit the secret resource.
Example of tls secret:
|
|
Exposing the service object with Ingress
I am using a Kubernetes ingress resource to access the wiki outside the internal cluster network. Think of the ingress like a proxy server that sits between the Kubernetes cluster container network and the network where the nodes are connected which could be public or private. In a previous post I used a project called Kubespray to deploy a cluster which includes an ingress server based on nginx.
|
|
If you want to use HTTPS and encrypt connections, specify the certificate secret name in the spec.tls.hosts.secretName from the previous optional step.
If using an ingress, create DNS records on your local network to point host (A) records to your Kubernetes worker nodes. Incoming traffic to ports 80 and 443 on those nodes will be intercepted by the ingress web server and routed to the appropriate cluster service. This is also often where SSL/TLS will terminate if downstream cluster services are not using TLS.
Setting up Wiki
Once the container is running, navigate to the URL in your browser that matches a DNS record for the ingress:
|
|
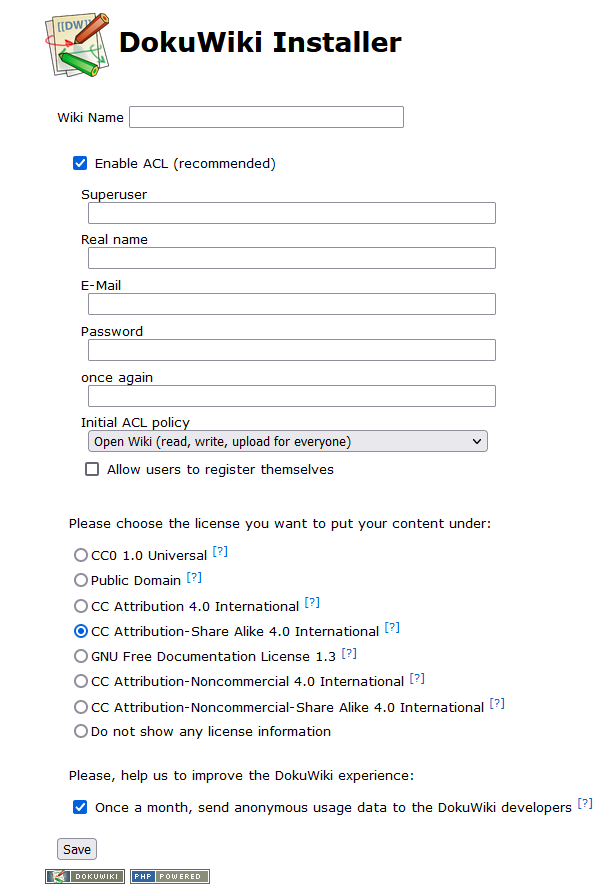
Once you have completed setup
First, restart the container
Get the name of the pod generated by the Deployment file:
|
|
Take the name of the pod for the following commannd to delete the running pod. When you delete the running pod, Kubernetes will create a new one then the wiki should start up with your configured settings.
Next, log in as an superuser and configure nice URLs
- login as the superuser created in setup and
- set “Use nice URLs” in the
admin/ConfigurationSettings panel to.htaccess - Check the box: Use slash as namespace separator in URLs to enable nice URLs.
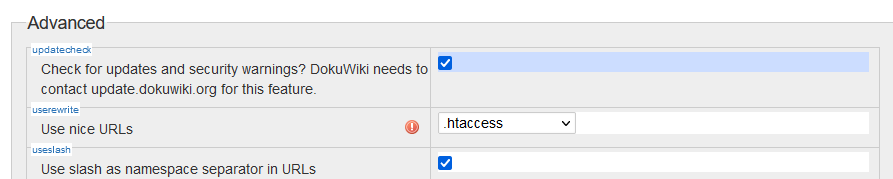
By default, DokuWiki does no URL rewriting, resulting in URLs like this:
http://wiki.example.net/doku.php?id=page
These URLs are considered ugly and are not indexed well by some search engines. Configuring “nice URLs” will make the page name featured in the URL instead of doku.php?id=page.
For more details on configurations possible, check out the Dokuwiki wiki.