Prometheus run on Kubernetes
On Kubernetes, you can run a Prometheus server by installing a Helm chart. If you are looking for information about what to do with Prometheus, check out a previous post to get an overview. This chart is maintained by the community and is available to browse on GitHub. There are a lot of options that can be configured with a values YAML file. This chart can also optionally install some other software such as Grafana, a node metrics exporter, and the kube state metrics server.
Backing up a bit, Kubernetes is an open source API/platform for managing container based workloads. Check out a previous post if you would like to learn more about what Kubernetes is.
Install kube-prometheus-stack
Prerequisites
- A Kubernetes cluster, probably at least v1.28 but older releases will work.
- Helm 3 installed on a system where you can download the community helm chart.
Prepare the helm chart
helm repo add prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo update
helm search repo prometheus-stackThis should show the latest release of the prometheus stack:
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION
prometheus-community/kube-prometheus-stack 66.3.1 v0.78.2 kube-prometheus-stack collects Kubernetes manif...
prometheus-community/prometheus-stackdriver-exp... 4.6.2 v0.16.0 Stackdriver exporter for PrometheusNow the chart can be installed with all defaults or you can customize with a values file or supply values with the command line.
To install the chart with all default options and create a namespace monitoring if it does not already exist.
helm install kube-prometheus-stack \
prometheus-community/kube-prometheus-stack \
--create-namespace -n monitoringConfigure prometheus
You can configure this Prometheus server by adjusting the Helm chart.
For example, here are the values that I supply to the helm chart for my cluster:
fullnameOverride: prometheus
prometheus:
prometheusSpec:
additionalScrapeConfigs:
# This is a proxmox prometheus exporter that I am scraping
# using this prometheus server
- job_name: "proxmox"
static_configs:
- targets:
- proxmox.example.com
metrics_path: /pve
params:
module: [default]
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__address__]
target_label: __param_target
- source_labels: [__param_target]
target_label: instance
- target_label: __address__
replacement: pve-exporter.monitoring.svc.cluster.local:9221
retention: 2d
remoteWrite:
# This configures the prometheus container to write all
# metrics to a remote server endpoint
# in my case this is another promtheus server on another system
- url: https://server.example.net/api/v1/write
serviceMonitorSelectorNilUsesHelmValues: false
storageSpec:
# At one point I tried to use nfs storage
# for prometheus. You can uncomment this
# if you have nfs or change the storageClass
# to something on your cluster
# Otherwise, prometheus will use an emptyDir volume
# since I remote write metrics I do not care about the
# durability of the prometheus storage inside k8s
# volumeClaimTemplate:
# spec:
# storageClassName: nfs-client
# resources:
# requests:
# storage: 40Gi
grafana:
defaultDashboardsTimezone: "America/Chicago"
grafana.ini:
feature_toggles:
enable: tempoSearch
ingress:
enabled: true
hosts:
- grafana.example.com
tls:
- secretName: tls-lan
hosts:
- grafana.example.com
persistence:
type: statefulset
enabled: sts
size: 2Gi
storageClassName: openebs-hostpath # Requires openebs
datasources:
datasources.yaml:
apiVersion: 1
datasources:
- name: Loki
type: loki
uid: Loki
access: proxy
editable: false
url: http://loki.monitoring:3100 # requies loki installed in cluster
jsonData:
# To setup integration between Loki and Tempo
derivedFields:
- datasourceUid: Tempo
matcherRegex: "(?:traceID|traceId)(?:=|\\s)(\\w+)"
name: TraceID
url: "$${__value.raw}"
- name: Tempo
type: tempo
uid: Tempo
access: proxy
editable: false
url: http://tempo-gateway.monitoring:80 # requires tempo installed in cluster
sidecar:
dashboards:
enabled: true
label: grafana_dashboard
folder: /tmp/dashboards
searchNamespace: ALLThere is a lot to unpack here but all of this set up here is a result of other software I have in my homelab. Previously I have set up Grafana Loki for aggregating logs, Grafana Tempo for collecting traces from applications, and I have set up Prometheus and Grafana to run outside of Kubernetes. Check out those linked posts for more background on those projects.
Install with argoCD
I use argoCD to deploy helm charts in my cluster and the config files are stored in a git repository. My argoCD application spec is the values file above along with a few options for argoCD. Here is an example argoCD application custom resource that I deploy:
---
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: prometheus
namespace: argocd
spec:
destination:
namespace: monitoring
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
project: default
source:
chart: kube-prometheus-stack
repoURL: https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts
targetRevision: 61.3.1
helm:
values: |
fullnameOverride: prometheus
prometheus:
prometheusSpec:
additionalScrapeConfigs:
# This is a proxmox prometheus exporter that I am scraping
# using this prometheus server
- job_name: "proxmox"
static_configs:
- targets:
- proxmox.example.com
metrics_path: /pve
params:
module: [default]
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__address__]
target_label: __param_target
- source_labels: [__param_target]
target_label: instance
- target_label: __address__
replacement: pve-exporter.monitoring.svc.cluster.local:9221
retention: 2d
remoteWrite:
# This configures the prometheus container to write all
# metrics to a remote server endpoint
# in my case this is another promtheus server on another system
- url: https://server.example.net/api/v1/write
serviceMonitorSelectorNilUsesHelmValues: false
storageSpec:
# At one point I tried to use nfs storage
# for prometheus. You can uncomment this
# if you have nfs or change the storageClass
# to something on your cluster
# Otherwise, prometheus will use an emptyDir volume
# since I remote write metrics I do not care about the
# durability of the prometheus storage inside k8s
# volumeClaimTemplate:
# spec:
# storageClassName: nfs-client
# resources:
# requests:
# storage: 40Gi
grafana:
defaultDashboardsTimezone: "America/Chicago"
grafana.ini:
feature_toggles:
enable: tempoSearch
ingress:
enabled: true
hosts:
- grafana.example.com
tls:
- secretName: tls-lan
hosts:
- grafana.example.com
persistence:
type: statefulset
enabled: sts
size: 2Gi
storageClassName: openebs-hostpath # Requires openebs
datasources:
datasources.yaml:
apiVersion: 1
datasources:
- name: Loki
type: loki
uid: Loki
access: proxy
editable: false
url: http://loki.monitoring:3100 # requies loki installed in cluster
jsonData:
# To setup integration between Loki and Tempo
derivedFields:
- datasourceUid: Tempo
matcherRegex: "(?:traceID|traceId)(?:=|\\s)(\\w+)"
name: TraceID
url: "$${__value.raw}"
- name: Tempo
type: tempo
uid: Tempo
access: proxy
editable: false
url: http://tempo-gateway.monitoring:80 # requires tempo installed in cluster
sidecar:
dashboards:
enabled: true
label: grafana_dashboard
folder: /tmp/dashboards
searchNamespace: ALL
# end of values
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
- ServerSideApply=trueTo install the helm chart with argoCD, I apply the above manifest to the cluster:
kubectl apply -f application.yamlUsing prometheus
You can use prometheus to collect many different types of metrics. Check out a previous post about prometheus and how to create graphs based on metrics collected using Grafana. After installing the helm chart, the Grafana server running inside the cluster will have some dashboards with Kubernetes metrics already populated. If you have used Prometheus elsewhere to collect system metrics with the node exporter, now Kubernetes nodes should also now have metrics available from the node exporter.
In my helm values, I supplied a configuration for an Ingress for Grafana. An ingress will create a load balancer or reverse proxy type configuration depending on your cluster to expose the Grafana server. You will need a DNS record that points to the hostname you provided in the ingress configuration. The other option is to use the kubectl utility to create a proxy from the Grafana service inside the k8s cluster to your local machine.
kubectl port-forward -n monitoring svc/prometheus-grafana 8080:80Unless you configure a password using the values file, the default credentials for this Grafana server will be username: admin, password: prom-operator
The server should prompt you to change the password when you first log in. Navigate to the Dashboards tab in the menu and you should see many Kubernetes dashboards.
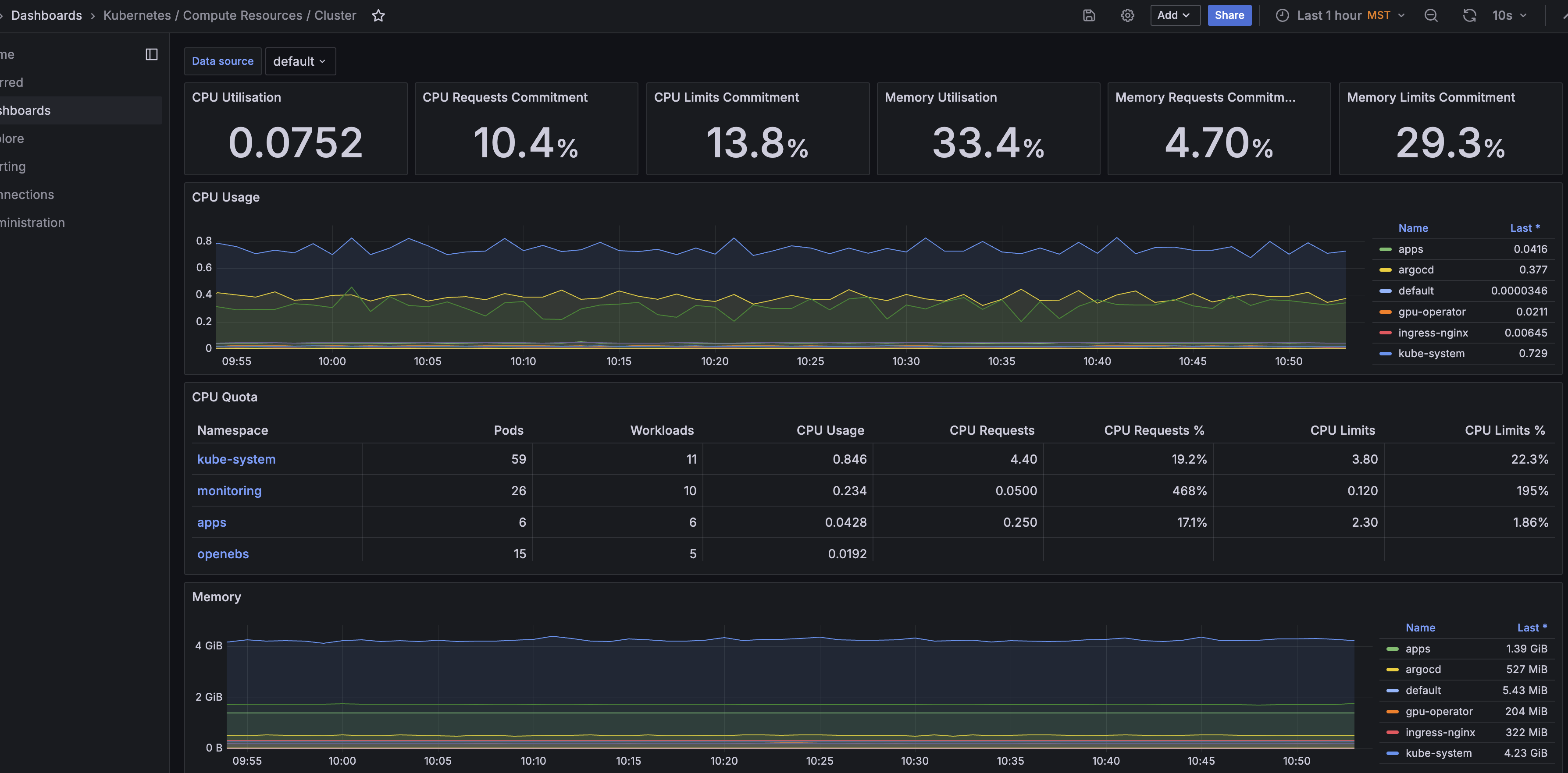
Here is an overview dashboard for compute resources in the cluster:
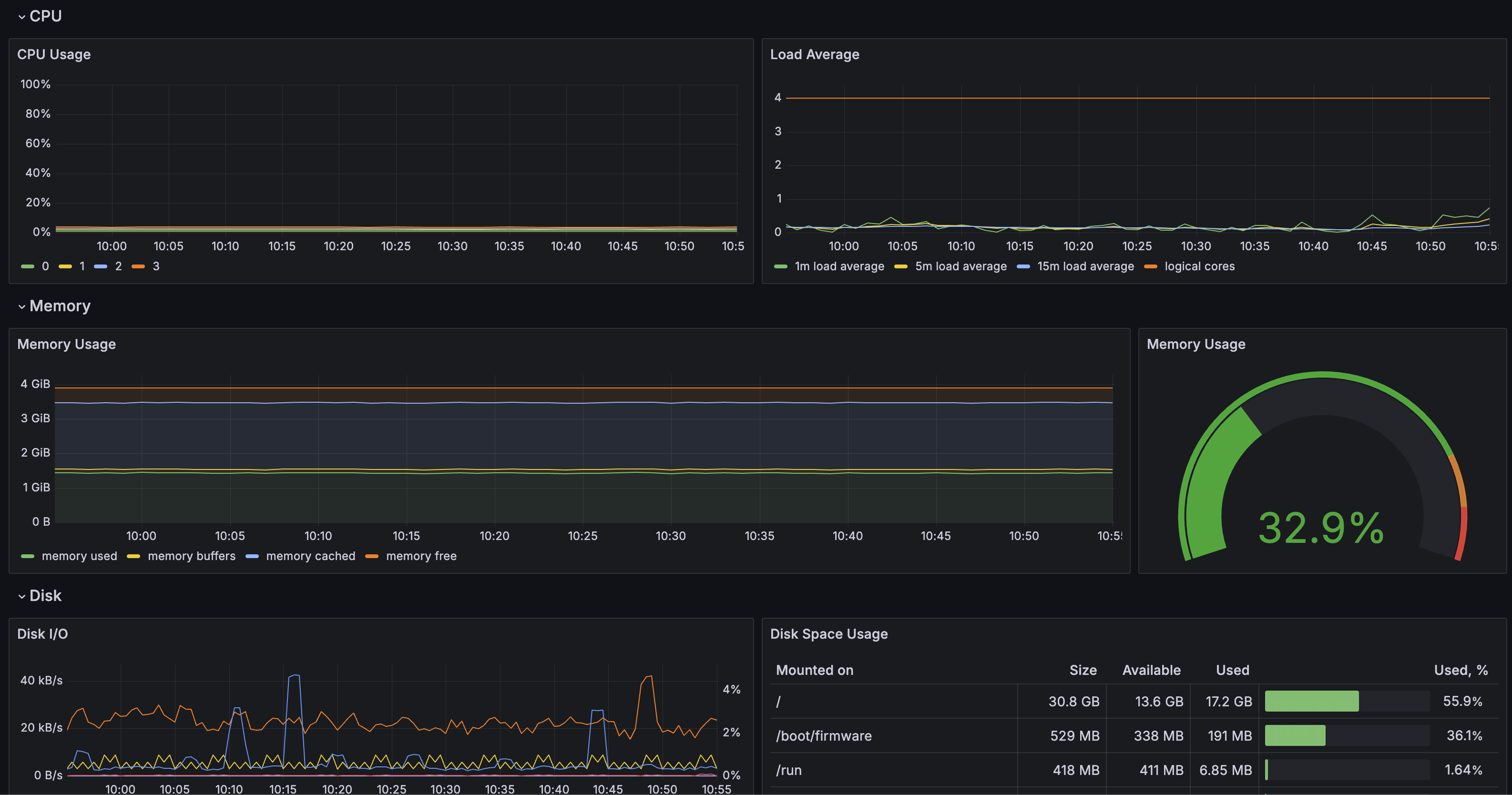
There should also be a node exporter dashboard: